The influx of Gen AI has taken the world of technology by storm. How can we forget, the jaw-dropping one million user base created by OpenAI’s ChatGPT just in the first week of its launch, setting a record-breaking benchmark for any other platform? This is good enough validation for the potential Gen AI brings to the table.
Gen AI slowly and steadily is making an impact on almost every industry, trying to support humans in bringing out better output with minimum effort. We are aware of how AI brought a seismic shift in the way businesses operate and use data to offer the best possible user experiences. With the entry of a new generation of Large Language Models (LLMs) what we also know as Gen AI, that exhibit human-like capabilities can do a lot in the realm of Supply Chain Management (SCM). But the million-dollar question is how prepared is supply chain management to onboard Gen AI in its operations?
The supply chain industry has relatively been slow in adopting Gen AI. But we cannot deny the fact it is catching up, as there is significant potential.
According to statistics shared by Gartner, 70% of business leaders believe that the benefits of Generative AI outweigh the risks. Supply chain leaders also mentioned that they are planning to allocate 5.8% of their budgets to technology and increase employee spending to deploy Gen AI. Whereas 65% of respondents to the Gartner survey mentioned, they will hire dedicated staff and experts to help deploy the technology in 2024.
The opportunities are endless!
This blog is mindfully curated to highlight how Gen AI is impacting the supply chain management space. We give our readers a deep understanding of how logistics 4.0 is way better than conventional SCM, by explaining Gen AI applications in modern supply chain management.
Before we get into the depths of the topic, let’s have a brief look at the digital supply chain process that consists of four stages as shown in the figure below:
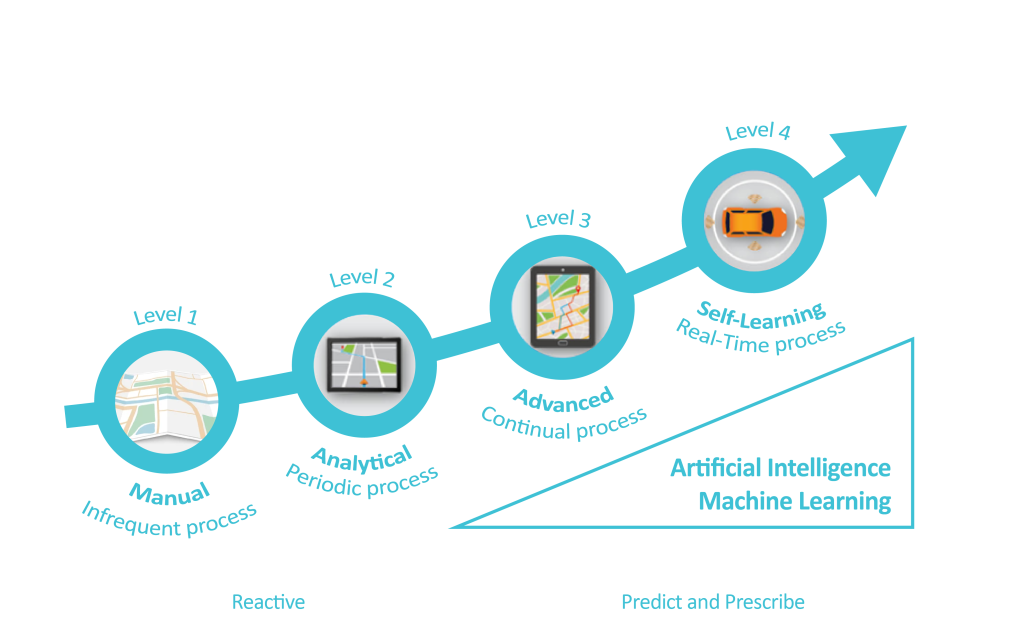
Supply chain is the backbone of practically every industry. Be it retail, manufacturing, healthcare, food, and beverage, or even IT, the supply chain is integral for uninterrupted and smooth operations. Operating as an extremely complex and intricate industry, traditional supply chain management that depends on old or obsolete systems and human intuitions is bound to face a saga of challenges.
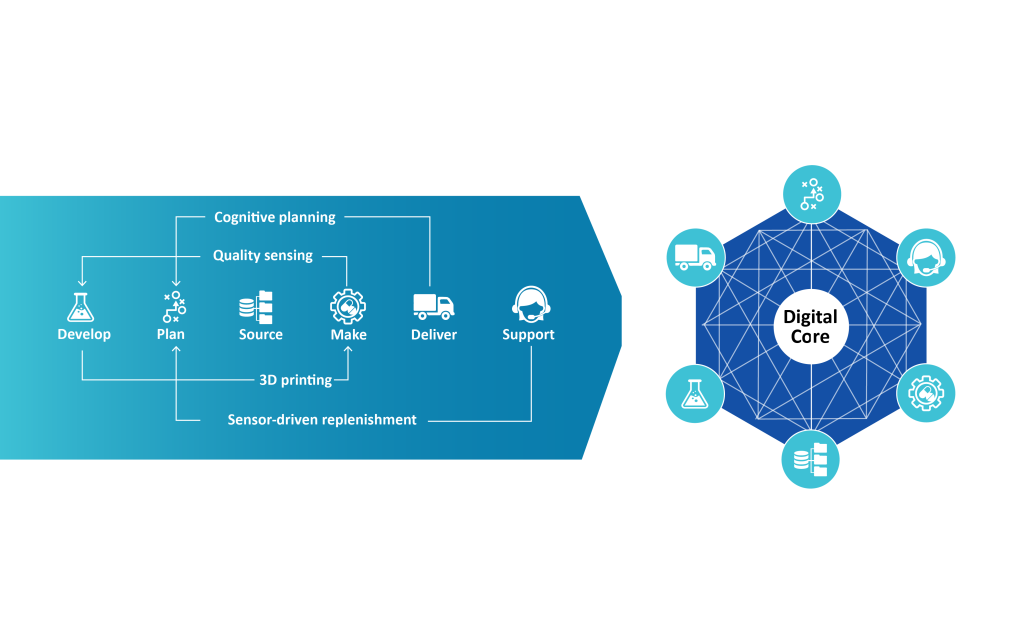
The figure gives a broad overview of implementing an intelligent supply chain in the logistics 4.0 era. It displays the shift from conventional linear architecture to a more dynamic, interconnected, and AI-enabled portfolio.
The traditional supply chain is now an outdated concept, and one of the primary issues in this setup is the lack of real-time visibility across the supply chain landscape, leading to inefficient decision-making and difficulty in prompt responses to disruptions. Additionally, legacy systems often struggle to integrate data from various sources, hindering the optimization of inventory levels and distribution routes.
Another challenge lies in forecasting demand accurately, as traditional methods may not effectively account for fluctuating consumer preferences or market trends. Moreover, manual processes increase the likelihood of errors and delays, impacting overall efficiency and customer satisfaction. These challenges highlight the pressing need for modernization and the adoption of advanced technologies in supply chain management.
Here is a brief view of challenges:
In supply chain management, one significant hurdle is the limited or sometimes complete lack of visibility across the chain. This gap makes it difficult to track the movement and status of goods effectively. Consequently, it leads to inefficiencies and potential disruptions.
Another critical challenge in the conventional supply chain management setup is the isolation and disconnection among different participants. When stakeholders operate in silos in the lack or absence of effective communication and collaboration, it is bound to hurt the smooth flow of goods and information, causing delays and misunderstandings.
The absence of robust product traceability and monitorability is one of the most pressing issues in the realm of supply chain. Without reliable systems to trace products’ journey and monitor their condition, ensuring quality control and timely delivery becomes daunting.
There is no alternative to transparency in supply chain operations, yet it’s often lacking. When information is not readily available or accessible to all relevant parties, it creates mistrust and inefficiencies.
Disorganized and untimely operations pose a significant challenge in supply chain management. Delays at various stages disrupt schedules, increase costs, and impact overall performance.
Calsoft dedicatedly works with a modern approach and understands that retail in the digital age is all about automation, and digital transformation focused on minimizing human intervention with cutting-edge AI-driven solutions. Get a glimpse of our potential offerings in retail on the digital front.
It is difficult to keep control of personal inventory these days, we can only imagine monitoring the intricate landscape of the supply chain with precision. Traditionally, supply chain management was an area that focused on attributes such as cost, speed, and quality. But with the outbreak of uncertainties such as the pandemic and most recently the Ukraine war has shifted the focus to prioritizing resilience from unforeseen circumstances, sustainability, and risk mitigation.
With Gen AI to the rescue, businesses now have the necessary tools to cope with this situation. Research projects that between 2023 to 2032 Gen AI in supply chain management is forecasted to reach a CAGR of 45.6%, leading to a surge in the total market value of Gen AI from $300 million to $12,941 million.
Now that we have a fair enough idea of the kind of impact Gen AI can have on supply chain, let’s dive deeper to understand Gen AI’s applications in Supply Chain Management. There is a range of Gen AI applications in SCM as displayed in the figure below. In this article, we will zoom in on the top five applications to deliver a clearer understanding.
The applications of Gen AI in supply chain management are endless. By exploring its potential, businesses can make smart use of the technology to model diverse strategies and streamline decision-making. Apart from the conventional options, Gen AI can also be tactfully deployed to come up with innovative packaging approaches. From designing eco-friendly materials to optimizing packaging shapes for efficiency, Gen AI opens doors to novel solutions that resonate with modern consumers and address evolving market demands.
The more you train Gen AI with constant trial and innovation, it can offer game-changing solutions to take the supply chain management game a notch higher.
Calsoft has been engaged in transforming businesses with the power of technology for over two decades with its AI/ML capabilities. We have partnered with a range of clients to help them transform every aspect of their business with state-of-the-art AI/ML solutions. So, whether you are looking for a cutting-edge solution or have complex supply chain management issues, we can support you in everything AI, right from ideation to execution.