The term Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become the talk of the town. Speaking of numbers, a report by Tech Jury confirms that 97% of mobile users are using AI-powered voice assistants. So, be it giving a voice command to Siri, the most favorite voice assistant for Apple lovers to help you find the best fine dining place in Vegas. Or receiving the most perfect online streaming show recommendation, after binge-watching all seasons of Money Heist, it is all about AI and its remarkable potential to understand human behaviors and preferences.
Recently, there has been a lot of hype built around AI. With Generative AI taking center stage, everybody is either talking about how good this technology is or worried about the potential concerns it raises.
Looking forward, it is impossible to deny the attention AI is gaining due to its transformative potential, which is making significant changes to various aspects of our lives. Not just this, but AI is powerfully revolutionizing every industry. In finance, AI algorithms are making a significant impact on investment strategies. In healthcare, robotic surgeries driven by AI systems are adding to precision and success rates by minimizing errors and leading to safer procedures, and the list goes on.
Also, it is important to know that AI is a concept that has existed for many years. But recent buzz with tools like ChatGPT, Bard, and more have put it under the spotlight. So, it is time to understand this technology from the bottom up. Our blog is thoughtfully curated to help readers get right the basics of AI by focusing on aspects like subsets, types, and future trends in AI.
AI is a concept that represents a noteworthy advancement in technology. Aiming to mimic human intelligence processes based on algorithms, this upcoming field within computer science works rigorously to develop machines capable of carrying out tasks traditionally taken care of by humans. A classic example of that would be driverless cars. Additionally, by using the potential of AI, it is now possible to train machines to stimulate complex cognitive functions for better problem-solving abilities.
There are various steps involved in the AI system’s function. This includes data collection, data cleansing and preparation, selecting appropriate algorithms for data processing, training, and testing the AI model, deploying the model into real-world use cases, and continuing the learning process to learn, adapt, and evolve. This workflow helps the AI system function efficiently and accurately.
Talking about their operation, AI systems work by combining large sets of data with intelligent, iterative processing algorithms to recognize patterns and features within the analyzed data. With each iteration of data processing, AI evaluates its performance, gathering additional expertise. This persistent processing capacity enables the system to seamlessly work on numerous tasks and acquire proficiency in various domains in very little time.
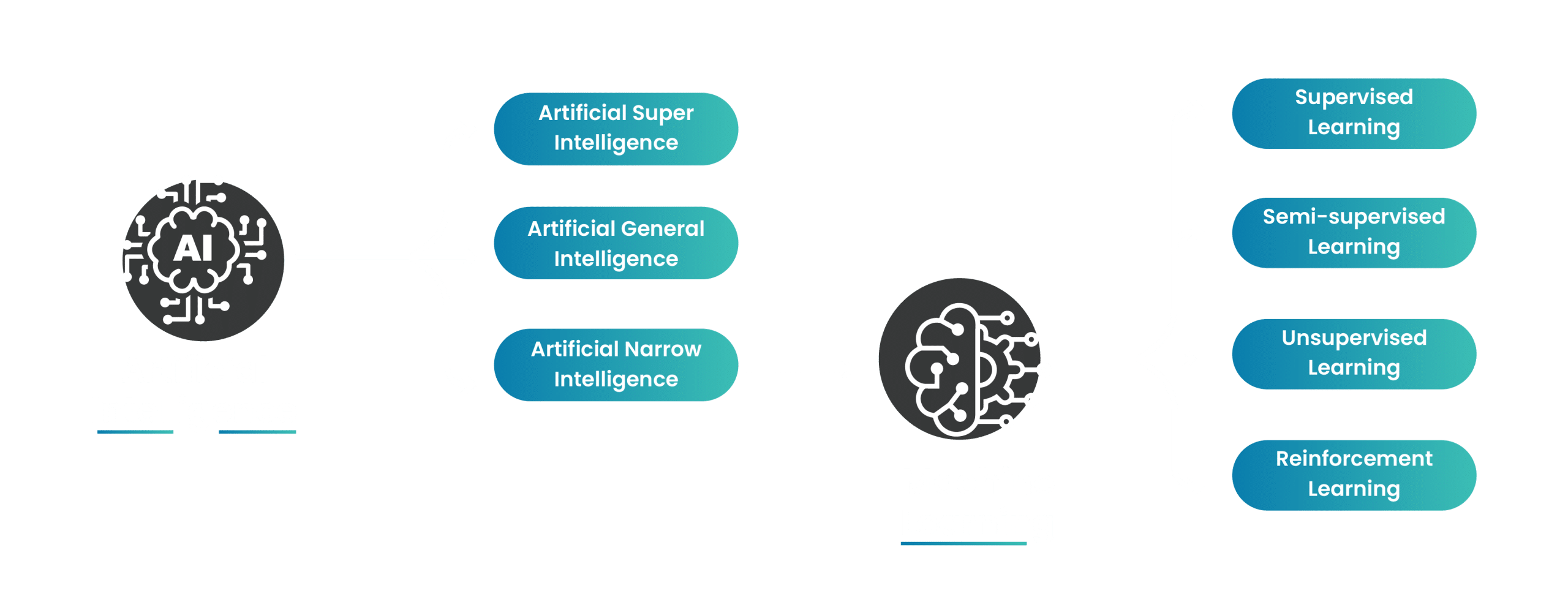
The primary goal of AI science is to deliver computer systems capable of replicating human behavior to be able to use human-like thinking processes to resolve complex issues. To achieve this goal in the best possible manner, AI systems make use of three types of learning paradigms – supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement to develop algorithms to offer solutions, suggestions, and predictions.
Despite the buzz AI is making, there is still a lot of confusion about what AI is and how to use it for a competitive advantage. This is why it is essential to have a good understanding of the six main subsets.
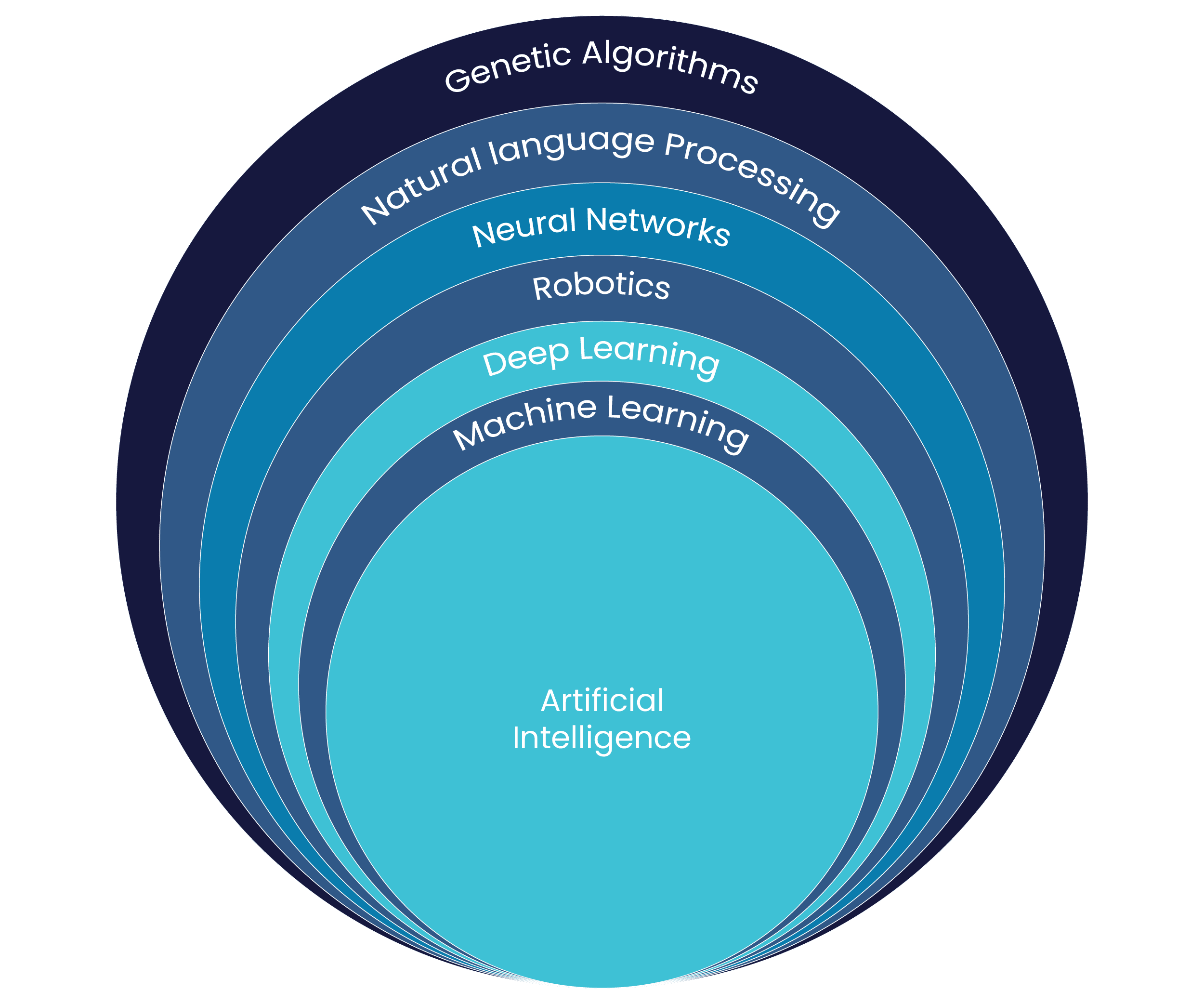
Machine Learning, also known as ML is often used interchangeably with AI. However, it is essential to understand that ML is a subset of AI that helps computer systems learn from experience and data without having to be explicitly programmed. There are different types of ML algorithms, but the most common ones are regression extensively deployed to predict outcomes and classification algorithms are used to group data and find patterns. Furthermore, these algorithms can be divided into supervised and unsupervised categories.
Deep learning, more specifically is a subset of ML. However, this subset has garnered attention for its prominent success in areas such as computer vision and speech recognition. Built with interconnected layers of processing nodes, deep learning networks are unique as they learn complex patterns in data by adjusting connections between neurons in every layer. An interesting piece of trivia about deep learning is that the more data it uses, the better the network will be at delivering a task that it is trained to do. Another advantage this AI subset brings is its ability to recognize patterns that are way too complex for human minds, making them suitable for tasks like natural language processing and image recognition.
AI systems largely exist as intangible entities. They operate through lines of code to process data and make decisions. However, robotics is one such subset of AI, that can be deployed physically and used to control objects in the tangible world. Built with a mix of supervised and unsupervised learning, robotics is often used for distinct functions that comprise automating manufacturing processes and enhancing safety by taking on challenging and dangerous tasks.
Neural networks are a subset of AI used to develop software that can mimic cognitive human functions, by processing data through interconnected nodes able to identify complex patterns just like the human brain. The scope of neural networks is vast and can be deployed to improve decision-making in a range of industries such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and more. Additionally, neural networks can also be put to use to enhance the accuracy of predictions delivered by ML algorithms. Unlike deterministic programs, neural networks are probabilistic and adept at handling intricate data.
Natural Language Processing or NLP takes care of the comprehension and manipulation of human language. It is an extremely interesting subset of AI that has been around for quite some time but has gained popularity due to the rapid and unstoppable innovation happening with ML and deep learning. Used for a large variety of applications such as sentiment analysis, text classification, and personal assistants, NLP proves to be an extremely powerful tool.
Popular applications such as Google Translate, Alexa, and Siri are classic examples of personal assistants that use NLP to comprehend and respond to human language.
Genetic Algorithms (GAs) play a vital role in finding solutions to optimization issues by simulating the process of natural selection. As GAs continue to evolve, it is essential to understand the way organisms that are well-adjusted to the environment have higher chances of survival and reproduction, similarly, GA solutions that are well-fitted for a problem are more likely to be chosen for and reproduced to get to an optimal solution gradually. Technically there are various ways to execute a GA, but the most common process typically consists of initialization, evaluation, selection, and reproduction.
Various types fall under the broad category of AI. Each type has its own set of differentiating characteristics and capabilities, and understanding the differences between them is crucial in comprehending the potential uses and limitations of AI technology.
Given the ongoing innovation and discoveries, AI is predominantly divided into several different types or categories based on various capabilities, functions, and underlying technologies.
Narrow AI, or Weak AI, refers to a category of AI system that is designed to perform a limited set of tasks. Regardless of its limitations, it is known to be one of the most common and widely used types of AI. Its applications range from facial recognition, image recognition, speech recognition, recommendation systems, and natural language processing (NLP).
Narrow AI is designed using machine learning algorithms, that are trained on extensive data sets to identify patterns and make predictions. These algorithms are engineered to perform a specific set of tasks like identifying objects or translating languages.
The concept of General AI still falls under theoretical AI research that is focused on creating software that can mirror several aspects of a real human being. For example, multitasking, independent thought processes, decision-making ability, and even emotions.
The most intriguing benefit of General AI will be its ability to perform tasks that require creativity, intuition, empathy, and emotions, which will open up new possibilities in areas like healthcare, art, and education. The most common examples of General AI are voice assistants like Siri, and ChatGPT a natural language processing tool.
Reactive machines are AI systems that don’t have a memory and are task-oriented, this means that an input always delivers the same output. ML models are prone to being reactive machines because they take customer data, such as purchase or search history, and use it to deliver recommendations to the same customers.
This type of AI is considered reactive. It performs “super” AI because the average human would fail to process huge amounts of data such as a customer’s entire browsing history and give customized feedback recommendations.
As the term suggests, limited memory AI systems have a small amount of memory that allows them to store information for a short period. These systems can use past experiences to inform their current decisions but still lack long-term learning capabilities. A typical example of limited memory AI is virtual personal assistants such as Siri or Alexa.
Getting the gist of different types of AI is crucial to have a fair idea about its capabilities and limitations. As technology advances and newer developments enter the AI realm, it is legit to expect more sophisticated forms of AI to emerge in the future. However, to stay in sync with innovation and advancement it is equally important to keep a close eye on what’s trending to benefit the most from this technology.
According to PrecedenceResearch, the global AI market is projected to reach $1.85 trillion by 2030. MIT Sloan Management states that 9 out of 10 organizations use AI to give them a competitive edge. Looking at the increase in the rapid development and adoption of this buzz-worthy technology, organizations need to stay accustomed to what’s happening in the arena to make the most of it.
In common terms, Multimodal AI refers to AI systems that have the potential to understand, analyze, and create information based on different types of data like text, audio, videos, and images. Different from traditional AI models this genre of the technology combines two or more modalities to furbish more comprehensive outputs. They indeed promote efforts towards mimicking the natural ability of human beings to process and deal with diverse sensory information.
Experts like Mark Chen, head of frontiers research at OpenAI state, that interfaces of the world are multimodal, and we look forward to models to see and hear what we as humans do and generate content that can potentially appeal to more than one of the human senses. The ultimate goal is to present better predictions based on data or information acquired from different modalities.
Small language models or SLMs are gaining recognition at a faster rate and are now on the list of future trends compared to their adaptability to large language models or LLMs. SLMs are engineered to display more competitive performance while working with fewer computational resources making them a better commodity for deployment in more constrained environments such as mobile devices and edge computing platforms. Additionally, the reduction in size also plays a vital role in facilitating quicker training, development, and deployment of AI apps across distinct domains.
Another interesting aspect of SLMs is that it is developer friendly as it allows them the scope to scale their models to fit a specific use case without having to compromise on performance. This flexibility is like a boon, especially in situations where computational resources are scarce or where real-time processing is a must.
Even though they are known as small language models, they are large enough to accommodate several billion parameters in LLMs but are convenient and small enough to easily be run on a mobile device offline.
Explainable AI or XAI is a set of techniques and processes that enable the comprehension of the rationale behind the output of an ML algorithm. In simple terms, it is a tool that can potentially have answers to questions like why and how it relates to AI systems and can be extremely helpful in addressing legal and ethical concerns.
As a result, AI researchers have recognized XAI as one of the necessary features of trustworthy AI and this area has also witnessed a surge in the attention quotient. Even though XAI is getting a generous amount of limelight, we cannot deny the limitations it comes with.
Saving the best for the last, GenAI or Generative AI is one of the most happening trends that has caught pace like never before. By utilizing a vast range of AI techniques and models designed GenAI is engineered to potentially create human-like content across various formats like text, image, and video. Additionally, it employs evolutionary algorithms, genetic programming, and neural networks to solve complex optimization problems and simulate natural selection processes. Leveraging genetic algorithms, it evolves solutions iteratively, selecting the fittest candidates and mimicking genetic inheritance for problem-solving. With its adaptive and self-improving nature, GenAI promises groundbreaking advancements in fields like optimization, machine learning, and robotics.
Life is unimaginable without AI. Gone are the days when driverless cars or human look-alike robots were a part of a sci-fi movie. The research and advancement in this technology genre have taken over almost every industry, however, to harness the power of AI responsibly and ethically it is inevitable to get its basics right.
Today organizations are increasingly relying on AI for its transformative benefits. So, whether you are building a cutting-edge AI/ML platform or want to use these technologies to accelerate digital transformation, Calsoft with its extensive knowledge and expertise can help you with all your AI/ML needs.